
FMGE or Foreign Medical Graduate Exam is an important exam for those Indian students who want to practice in India after pursuing MBBS Abroad. The National Board of Examination conducts this exam twice a year. FMGE assess the knowledge and skills related to medical education of applicants.
FMGE is an essential exam for foreign medical graduates seeking to practice in India. It comprises of two papers, each with 150 multiple-choice questions, and is conducted twice a year in June and December. Candidates must score at least 150 out of 300 to pass.
Mode of application is online and fees for General category candidates is INR 6,195/- , exam duration is of 6 hours, online mode.
The previous year’s papers not available due to the restriction about the candidates who sit in this exam is that they cannot post the papers in any form online/offline otherwise penalise.
Eligibility criteria:
- Must hold an MBBS or equivalent degree from a recognised foreign Institution.
- Above MBBS degree must be recognised by India Medical council Act , 1956.
- Candidate should have the proof of the completion of the medical program.
- Must be citizen of India or hold overseas citizen of India (OCI) status.
- Achieve the minimum score in a language proficiency test specified by the MCI.
After passing MCI Screening Exam, during internship the students may appear NEET-PG if they want to pursue post-graduation (MD/ MS/ DNB/ Diploma). From 2023, FMGE & NEET-PG will be merged & replaced by NEXT: National Exit Test which will be a common exit exam for MBBS, Indian as well as Foreign Medical Graduates
Pattern of FMGE Exam
There are total two parts i.e. Part A and Part B in exam.
Exam is of multiple choice type questions having 300 question of 1 mark each and equally distributed in Part A and Part B and no negative marking if wrong and no mark allotted if not attempted. Total time for exam is of total 5 hours in 2.5 hours in both shifts.
To get the certificate , a candidate need to get 150 marks out of 300 marks.
After passing MCI Exam for Foreign Medical Graduates, students have to undergo compulsory 1 year rotatory internship in India after which they get permanent registration with MCI (MCI is now coined as NMC: National Medical Commission) or State Medical Council. The difficulty level of FMGE: Foreign Medical Graduate Examination (MCI Screening Exam) is comparatively high & is similar to NEET-PG.

FMGE Syllabus :
The FMGE syllabus includes total 19 subjects which are further divided into subtopics.
ANATOMY
- General Anatomy: Basic tissues to the body, Terminology & Nomenclature
- Elements of Anatomy: Osteology, Arthrology, Myology, Angiology, Neurology
- Regional Anatomy: Upper limb, Lower limb Thorax-including diaphragm Abdomen and Pelvis, Head, Neck Brain, and Spinal cord
- Embryology: Development of individual organs and systems, Postnatal growth & development
- Histology: General Histology Microanatomy of individual organs and systems
- Human Genetics: Principles of Human Genetics and Molecular Biology
- Radiological Anatomy: Skiagrams, Special X-rays, Principles of imaging techniques.
- Surface Anatomy: In cadavers, in the living
- Sectional Anatomy: Thorax, Abdomen, Head, Neck, and Brain
PHYSIOLOGY
- General Physiology
- Body fluids – Blood
- Nerve and Muscle
- Gastrointestinal Tract
- Kidney
- Skin and Body temperature
- Endocrine Glands
- Reproduction
- Cardiovascular System
- Respiratory System
- Central Nervous Systems
- Special Senses
BIOCHEMISTRY
- Cell and Sub-cellular structures
- Hydrogen Ion concentration Acid, Bases, Buffers, Handerson-Haselbach equation
- Isotopes and their Application
- Carbohydrates
- Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
- Lipids
- Nuclear Acids
- Enzymes
- Vitamins
- Biological Oxidation
- Digestion and Absorption from GI Tract
- Intermediary Metabolism
- Carbohydrate Metabolism
- Lipid Metabolism
- Protein and Amino Acid Metabolism
- Purine and Pyrimidine Metabolism
- Minerals
- Biochemical Genetics and Protein Biosynthesis
- Tissue Biochemistry
- Liver Functions
- Nutrition and Energy Metabolism
PATHOLOGY
- Cell injury
- Inflammation and Repair
- Immunopathology
- Infectious diseases
- Circulatory disturbances
- Growth disturbances and Neoplasia
- Nutritional and other disorders
- Genetic disorder
- Hematology
- Cardiovascular Pathology
- Respiratory Pathology
- Pathology of Kidney and Urinary Tract
- Hepato-Biliary Pathology
- Lymphoreticular System/Spleen
- Reproductive System (Male & Female)
- Diseases of the Breast
- Musculoskeletal System
- Endocrine pathology
- Neuropathology
- Dermato-Pathology
- Ocular Pathology
MICROBIOLOGY
- General Microbiology
- Immunology
- Bacteriology
- General Virology
- Systemic Virology
- Mycology
- Parasitology
- Clinical/Applied Microbiology
PHARMACOLOGY
- General Pharmacology
- Autonomic Nervous System
- Cardiovascular System
- Diuretics
- Drugs affecting blood and blood formation
- Autacoids and related drugs
- Respiratory System
- Gastro-intestinal System
- Endocrine pharmacology
- Central Nervous System
- Psychopharmacology
- Drugs in Anaesthetic practice
- Chemotherapy
- Toxicology
- Clinical Pharmacology and Rational drug use
FORENSIC MEDICINE
- Definitions
- Courts of India
- Court procedures
- Medical Certifications & medico-legal reports including the dying declaration
- Death
- Changes after death Inquest by police, magistrate, and coroner Identification
- Examination of mutilated human remains
- Medico-legal autopsies
- Mechanical injuries and wounds
- Examination of an injury case
- Injuries due to physical agents & their medico-legal importance
- Asphyxial death
- Death due to malnutrition, neglect battered babies
- Dowry death
- Virginity, sexual offences, sexual perversions
- Legitimacy
- Pregnancy and delivery
- Infanticide
- Biological fluids
- Seminal stains
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Medical Jurisprudence
- Toxicology
GENERAL SURGERY
- Haemorrhage and shock
- Fluid, electrolyte, and Acid balance, nutrition Skin tumours, burns, skin grafting
- Arterial diseases
- Venous diseases
- Lymphatic and Lymph nodes
- Wounds
- Specific and non-specific injections
- Tumours, Cysts, Ulcers, Sinuses, and Fistulae
- Infections of the Hand and Foot
- Diseases of muscle, tendons, bursae, and fascia Hernia
- Umbilical granuloma, fistula, adenoma
- Abdominal Wall
- Face, Teeth, Gums, Mouth, Tongue, Salivary glands, Neck
- Thyroid Glands, Thyroglossal Tract and Endocrines
- Breast
- Sympathetic System
- Cranio-Cerebral injuries
- Brain, Nerves
- Genito-Urinary System
- Kidneys and Ureters
- Urinary Bladder
- Prostrate
- Urethra
- Penis, Testis, and Scrotum
- Vasectomy and Recanalization
- Cardiothoracic System
- Oesophagus, Stomach, and Duodenum
- Spleen, Liver, Gall Bladder and bile ducts Pancreas
- Peritoneum
- Intestines, intestinal obstruction
- Appendix
- Rectum and Anal Canal
ANESTHESIA
- Anatomy of upper airway
- Physiology of Respiration O2/CO2
- Methods of oxygen therapy.
- Pre-operative evaluation/pre-medication
- Anaesthetic agents, stages of Anaesthesia
- Principles and mechanism of administration of general anaesthetics, balanced Anaesthesia
- IPPV, Endotracheal Intubations
- Muscle Relaxants
- Spinal/Epidural Anaesthesia
- Local Anaesthesia
- Cardiopulmonary resuscitation basic, use of simple ventilators
- Monitoring
- ICU, the role of anaesthesiologist in ICU
- Shock
- Blood Transfusion and Fluid Electoral
- Balance Sites of respiratory obstruction and Management of the Airway in an unconscious patient
- Poisoning
- Role of anaesthesiologist in acute and chronic relief.
ORTHOPEDICS
- Traumatology
- Injuries to bones and joints
- Injuries of the Lower Extremities
- Injuries of the Spine Vascular Injuries
- Cold Orthopaedics
- Regional Conditions
- Neuro-Muscular Disorder
- Bone and Joint Tuberculosis
- Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation
RADIO- DIAGNOSIS
- Respiratory System
- Cardiovascular System
- Gastrointestinal System
- Obstetrics &Gynaecology
- Skeletal System
- Central Nervous System
- Excretory System
RADIOTHERAPY
- Principles of Radiotherapy
- Principles of Chemotherapy
- Prevention and Early Diagnosis of Cancer
- Principles of Nuclear Medicine
- Common radiation reactions and management
- Radiotherapy and chemotherapy in commonly seen cancers
- Radio-isotopes in diagnosis and therapy
PEDIATRICS
- Vital statistic
- Neonatology Growth & Development
- Nutrition
- Infections
- Genetics
- Paediatric Emergencies
- Central Nervous System
- Gastroenterology
- Nephrology
- Endocrinology
- Respiratory System
MEDICINE
- Clinical Methods in the Practice of Medicine
- Common symptoms of the disease
- Nutrition/Exposure to Physical & Chemical Agents
- Infections
- Haematology
- Respiratory System
- Cardio-Vascular System
- Gastro-Intestinal Tract
- Emergency Medicine
- Neurological System
- Nephrology & Urinary system connected to Tissue Disorders
- Endocrine System
- Geriatrics
TUBERCULOSIS AND RESPIRATORY DISEASES
Diagnosis and management of common ailments affecting the chest with special emphasis on management and prevention of Tuberculosis and National Tuberculosis Control Programme.
PSYCHIATRY
- History aspects and diagnosis & treatment of mental illness
- Conduction of Mental Status Examination
- Behavioral Sciences
- Different psychoses
- Clinical features, diagnosis, and management of:
- Schizophrenia
- Mania and depression
- Anxiety disorders and hysteria
- Dementia
- Alcoholism Drug Abuse
- Psychiatric emergencies
- Clinical features, diagnosis, and management of psychiatric disorders of childhood and adolescence
- Personality disorder
DERMATOLOGY AND SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED DISEASES
- Dermatological therapy
- Lichen Planus
- Diseases caused by Nutritional and Environmental Factors
- Infective Disorders
- Melanocytes, pigment metabolism, and other disorders of Pigmentation
- Allergic Disorders
- Dermatitis and Eczema
- Vesiculobullous Diseases
- Alopecia and Hirsutism
- Structure and Functions of Sebaceous Glands and Disease
- Leprosy
- Psoriasis
- STD
OPHTHALMOLOGY
- Basic sciences – Anatomy, Physiology, Pharmacology, Pathology, Elementary Optics, Diseases of the Eye
- Conjunctiva
- Cornea
- Sclera
- Uveal Tract
- Lens
- Vitreous
- Glaucoma
- Retina
- Optic Nerve
- Intra-Ocular Tumours
- Squint
- Orbit
- Lacrimal System
- Lids
- Refractive Errors
- Injuries
- Ophthalmic Surgery
- Community Ophthalmology
- Miscellaneous
OTORHINOLARYNGOLOGY
- Diseases of the Ear
- Diseases of the Nose and Para Nasal sinuses
- Diseases of Nasopharynx
- Diseases of Trachea
- Oesophagus
OBSTETRICS AND GYNECOLOGY
- Anatomy of the Female Reproductive Tract
- Physiology of conception
- Development of foetus and placenta Diagnosis of pregnancy
- Maternal changes in pregnancy
- Antenatal care
- Abnormal obstetrics
- Normal labour
- Normal puerperium
- Breast Feeding
- Care of new-born
- Medical termination of pregnancy
- Family planning
- Operative obstetrics
- Post caesarean pregnancy
- Pharmacotherapeutics in obstetrics
- Safe motherhood
- Maternal morbidity and morality
- Medico-legal aspects
- RCH
- Current topics
- Vaginal discharge
- Menstrual disorder Fertility, infertility
- Endometriosis and the Allied States
- Genital injuries and fistulae
- Genital infections
- Genital prolapse
- Tumours
- Carcinoma
- Radiotherapy in gynaecology
- Chemotherapy in gynaecology
- Endoscopy
- Diseases of breast
- Operative gynaecology
COMMUNITY MEDICINE
- Evaluation of Public Health and Concepts of Health
- Environment and Health Education
- Nutrition and Dietetics
- Occupational Health
- Medical Sociology and Community Mental Health
- Fundamentals of Biostatistics
- Basic Epidemiology
- Epidemiology of Specific Diseases
- Communicable and Non-Communicable Diseases
- Demography Reproductive and Child Health
- School Health
- Urban Health
- Health System in India
- Health Planning and Management including Disaster Management
- International Health
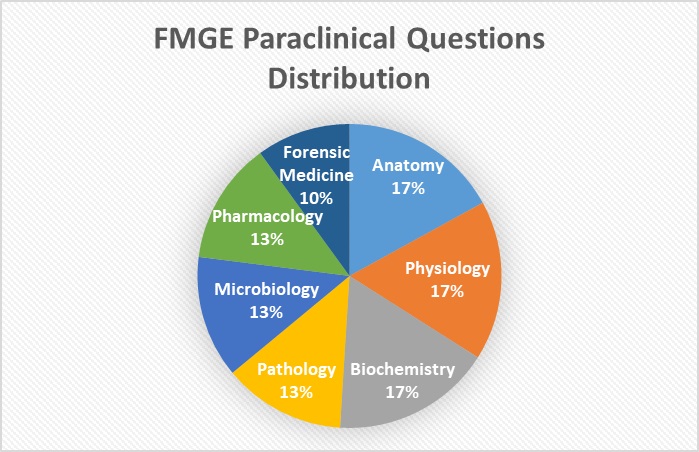
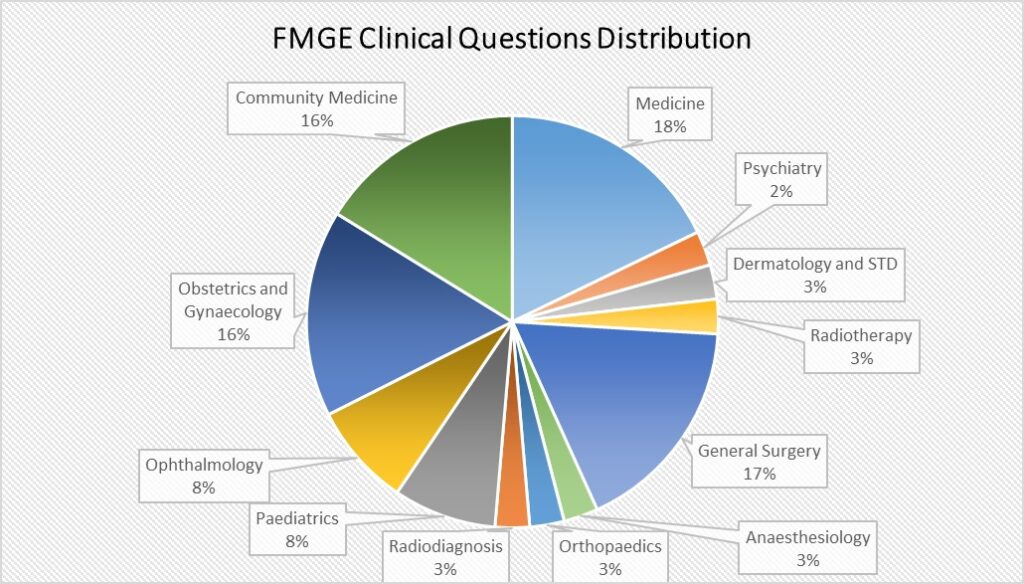
Marks Distribution Pattern:
One can check the distribution of marks according to the various subjects and prepare accordingly.
The FMGE preparation strategy
- Study in group, discussion among on the topics to clarify doubts, also take consultation with the subject experts on doubts.
- First devote your time in basic pre and para clinical subjects such as Physiology, anatomy, Pathology etc. and later prepare clinical subjects like medicine and surgery.
- More focus on clinical subjects as this section is of 200 marks out of total 300 marks.
- Revision is key to success of this exam, as the exam date approaches near a candidates should make a schedule for the revision of each topic, especially high grossing topics.
- Practice to solve sample multiple choice question papers under the same circumstances like of examination hall.
- Prepare the chart/poster of various topics and paste in front or side wall of bed side where one sleeps. In the morning recall those topics in a glance by referring these chart/poster.
- Download certain learning mobile/smartphone applications like Medix Learning APP , Prep Ladder etc. which provide questions of FMGE exams in a form of quiz. Take regularly some of those quiz to understand the subject matter.
- Take guidance from seniors who already qualified the exam for the final preparation , it will help to succeed in the FMGE in first attempt.
Sample Paper :
Click on below link to download the FMGE sample exam paper for the preparation .
Disclaimer :
This article provides general information about the Foreign Medical Graduate Examination (FMGE) and is intended for informational purposes only. It does not constitute professional advice. The information provided may change over time, and readers are advised to consult official sources for the most up-to-date guidelines and regulations. We cannot guarantee the accuracy or completeness of the information presented.


oi, gostei muito da sua escrita, compartilhe, entraremos em contato mais sobre seu artigo na AOL, preciso de um especialista nesta área para resolver meu problema Talvez seja você. Ansioso para vê-lo
Obrigado por apreciar meu blog, solicito que compartilhe sua oferta em relação ao trabalho que você precisa do especialista.
Mygreat learning Awesome! Its genuinely remarkable post, I have got much clear idea regarding from this post . Mygreat learning
Thanks for appreciaitng my blog. Also visit my another website http://www.mybeaudate.in
I was suggested this web site by my cousin Im not sure whether this post is written by him as no one else know such detailed about my trouble You are incredible Thanks
Thanks for appreciaitng my blog , I am trying to provide my website visitor about the information which helps freshers and experienced job searchers. Keep visiting and revewing my blogs and suggest others to gaim maximum benefits.